Website Optimizations Ten important strategies for website optimization
If these ten strategies for website optimization are implemented correctly, you are well on your way to success!

- Ten Essential Strategies for Website Optimization
- Search intention
- Technical SEO
- User experience
- Mobile first
- Core Web Vitals
- Schema.org
- Content Marketing
- Link building - Backlinks
- Test and document changes
- Tracking and analyzing KPIs
- Conclusion
Ten Essential Strategies for Website Optimization
Google was officially introduced 25 years ago, in 1998. A lot has changed since then, but one thing has remained the same. If you consistently focus on the most important factors of web optimization, you can still be very successful online.
Sure, the important factors have changed a lot compared to 1998 and it's become harder and harder to focus on what's important. That's why it has never been as important as it is today to be disciplined and focused when it comes to search engine optimization (and thus web optimization).
Now, of course, the following questions arise: Which factors should we focus on? Which factors can be used to improve search engine rankings? How can we build organic and sustainable traffic in a highly competitive environment?
This post is about introducing you to ten important web optimization strategies and showing you how to use them to optimize your website.
1. Search intention
As machine learning, artificial intelligence, and deep learning continue to evolve, each factor in Google's core algorithm will become more important.
Google's goal is to understand the context of a particular search query and deliver results that match the user's intent. This makes advanced keyword research and keyword selection more important than ever.
Before you spend time and resources trying to rank for a keyword, you need to look at the websites that are currently at the top of the SERPs (search results pages) for that keyword.
The contextual relevance of a keyword must match a search query. There are some keywords and search queries for which placement is impossible. For example, if Google has determined that people searching for "lawyer Zurich" want a list of lawyers in Zurich to choose from, a number of trusted lawyer directories will appear at the top of the SERPs. An individual or a single company will not be able to displace these directories, regardless of the optimizations made. In these cases, you need to refine your SEO strategy and adjust your content accordingly.
2. Technical SEO
The foundation for technical SEO is a solid website architecture.
You can't just publish a random collection of pages and posts and expect good rankings. An SEO-friendly website architecture guides users through a website and makes it easy for Google to crawl (read) and index a page.
Once you've built the right architecture and you can ensure that yours meets the needs of your users, it's time to perform a technical SEO audit.
Thanks to the many SEO tools available, a technical SEO audit is no longer a daunting task. However, it's important that you know how to interpret the data provided and what to do with it.
For the beginning, you should check the following points and fix any issues you uncover:
Look for status code errors and correct them.
Check the robot.txt for errors. Optimize it if necessary.
Check the indexing of your website via Google Search Console. Investigate and fix any issues discovered.
Fix duplicate meta titles and duplicate meta descriptions. Add missing metadata - all images must also be correctly labeled (alternate texts).
Check the content of your website. Check the traffic data in Google Analytics. Consider improving or deleting poor performing content.
Fix broken links. These are an enemy of user experience and have a negative impact on rankings.
Submit your XML sitemap to Google via Google Search Console.
3. User experience
User experience (UX) is about giving users the best possible experience on your website based on their needs, wants, and abilities. Good UX takes into account not only user needs but also business goals and objectives. According to Peter Morville, factors that influence UX include:
Useful - your content must be unique and satisfy the needs of your users.
User-friendly - your website must be easy to use and navigate.
Desirable - your design elements and brand should evoke emotion and excitement.
Findable - integrated design and navigation elements that make it easy for users to find what they need.
Accessible - content must be accessible to everyone - including the 12.7% of the population with disabilities.
Credible - your website needs to be trustworthy so users believe you.
Valuable - your website must provide value, both to the user in the form of a great experience, and to your business in the form of a positive ROI.
Multivariate and A/B testing are the best way to capture your website users' experience and discover potential optimizations.
Multivariate testing is best when complex changes are planned, as many different elements can be included and tested. In addition, it can be determined how the elements work together.
A/B testing, on the other hand, compares only two different elements on your website to determine which element works best.
4. Mobile first
Google officially began rolling out the mobile-first index in March 2018. However, smart marketers have been taking a mobile-first approach long before the official rollout, as more and more people are researching the internet from their smartphones.
Google Search Central's statement:
"Neither mobile-friendliness nor a responsive layout are prerequisites for mobile-first indexing. Pages without mobile versions will still work on mobile and can be used for indexing. Nevertheless, it's time to say goodbye to the desktop-only version and embrace the mobile version :) "
Below are some basic tips on how to make your website mobile friendly:
Adapt your website to any device - be it desktop, mobile or tablet.
Scale your images if you're using responsive design, especially for mobile users.
Use short meta titles as they are easier to read on mobile devices.
Avoid pop-ups that obscure your content and prevent visitors from getting a quick overview of your content.
On mobile, less can be more. In a mobile-first world, long content doesn't necessarily equate to more traffic and better rankings.
5. Core Web Vitals
In July 2021, the Page Experience Update was introduced and is now integrated into Google's core algorithm as a ranking factor.
As the name suggests, the Core Web Vitals initiative was developed to quantify the essential metrics for a healthy website. This aligns with Google's commitment to providing the best user experience.
According to Google, "Load experience (how fast does your site load), interactivity, and visual stability of page content together form the foundation of Core Web Vitals."
Each of these metrics focuses on a specific aspect of the user experience.
The Core Web Vitals are measurable and quantifiable. So objective measurements can help optimize your website.
Tools for measuring Core Web Vitals:
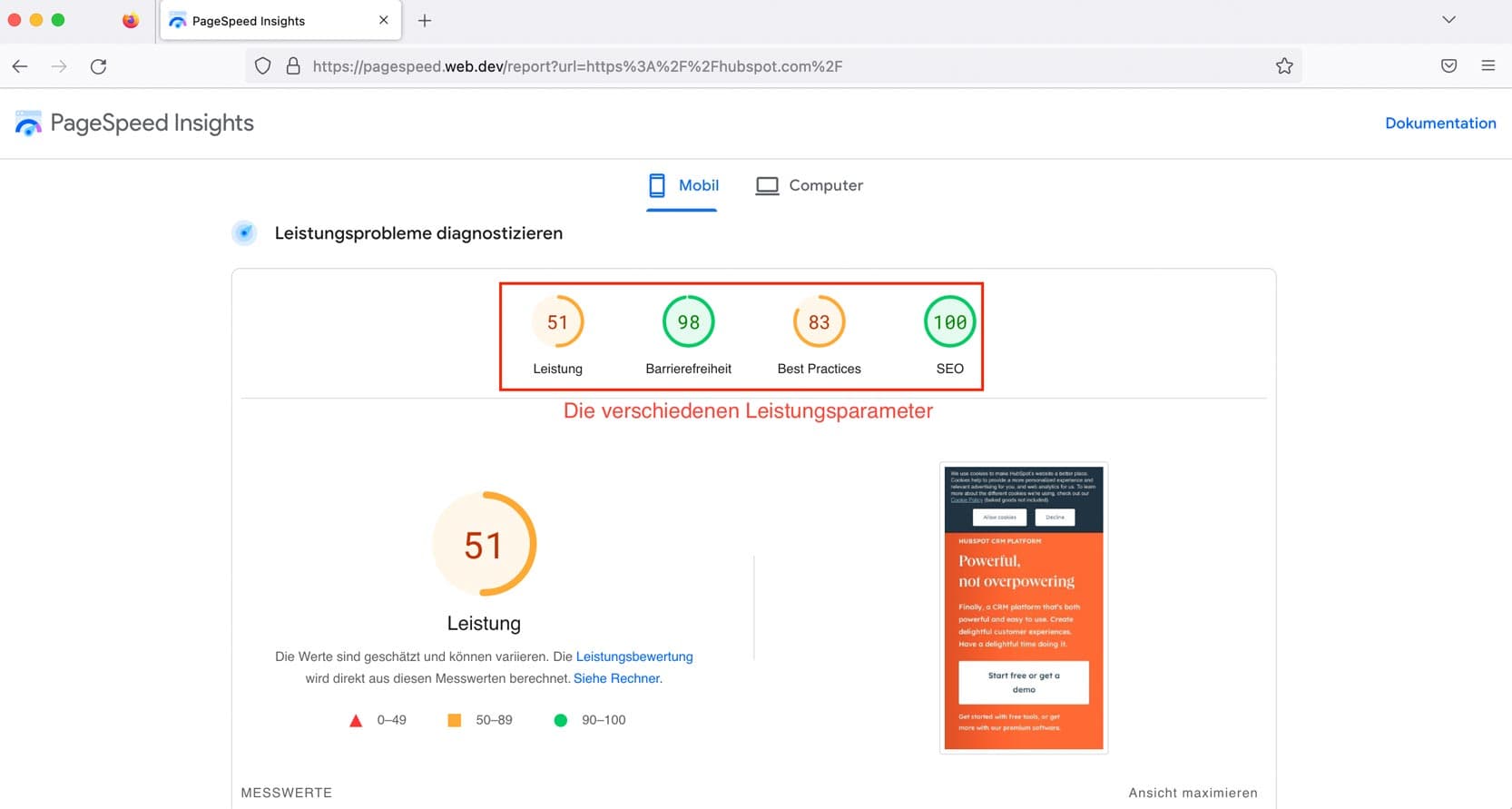
PageSpeed Insights: Measures both mobile and desktop performance and provides recommendations for improvement.
Lighthouse Test: an automated, open-source tool developed by Google to help developers improve website quality. Lighthouse Test has several features not available in PageSpeed Insights, including some SEO checks.
Search Console: A Core Web Vitals report is now included in GSC (Google Search Console). It shows URL performance by status, metric type, and URL group.
6. Schema.org
Schema is an HTML markup that you can use to structure your website content. By adding Schema structure, search engines can better read your website and add rich snippets to your organic search results. Rich snippets are supplemental information about your website. They are designed to help searchers answer the query in the best way possible, improving the search experience.
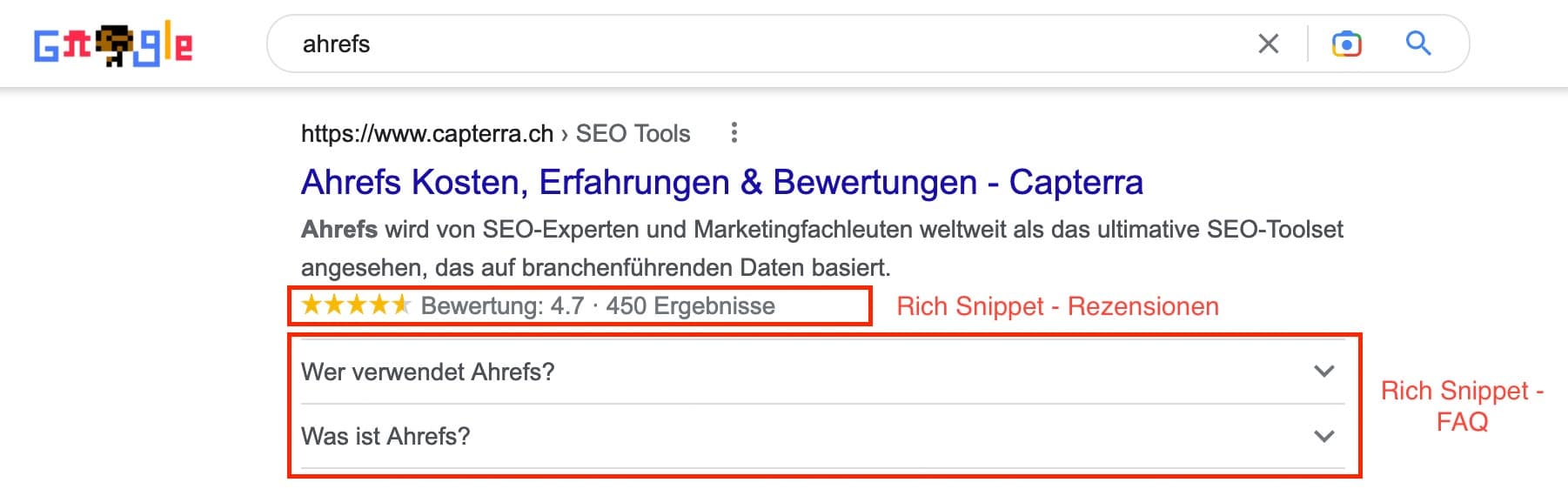
All leading search engines, including Google, Yahoo, and Bing, support the use of structured data (schema markup). However, there is no evidence that adding schema has any impact on rankings. However, search queries can be answered better and your search results provide more information to searchers. In addition, your visibility increases as your search results take up more space in the SERPs.
On schema.org you can find all the possibilities how to structure and markup your content. Here are some examples, which are often used:
Markup of single articles (products)
Breadcrumbs
Awards of your events
FAQs
Awarding of vacancies
Award of your logos
Award of recipes
Awarding of your reviews
Help with schema markup
You find the idea of structuring your site using schema.org intimidating?
7. Content Marketing
It is predicted that 97 zettabytes (one zettabyte equals 1,073,741,824 terabytes) of data will be created, captured, copied and consumed worldwide this year. By comparison, that's the equivalent of 18.7 trillion songs or 3,168 years of HD video per day.
The challenge of making your content stand out from this vast amount of data is enormous and requires some resources and good content strategies.
The following inputs will help you with that:
Create a content hub in the form of a resource center. This will help you better manage and plan your content.
Fill your content hub with a combination of useful, informative and entertaining content.
Write articles that build on existing articles and link to them. Make sure that the content always offers a clear added value from the user's point of view.
Distribute your created content in the social networks. Paid advertising can also be used to spread the content widely and quickly.
Pick up on trending topics that can be related to your subject area (such as products, services or services).
Rely on images and videos. Images and videos tend to convert better than plain text.
Keep your content current. This means that old content should be deleted or updated regularly.
8. Link building - Backlinks
Links are still an important ranking factor.
Over the years, search engines have become increasingly adept at recognizing and devaluing spam links. Spam links come from dubious or unsafe sites and should be consistently deleted via the Google Search Console.
Quality is much more important than quantity when it comes to backlinks.
The best link building strategies according to Hubspot include:
Offer high-quality content to potential link creators
Mention experts and influencers
Have experts contribute to content
Interacting with link creators on social media
Writing guest articles for other people's blogs
Give expert interviews
Comment on other people's blogs
Gather and prepare relevant data
Offer webinars, freebies or tools
Post job and internship opportunities on the website
Ask for links
Present at professional conferences and universities
Get links from non-profit organizations
Ask for subsequent linking
Link yourself
Become a Wikipedia expert
Detect and delete broken backlinks
Submit a rating online
9. Test and document changes
A recent study showed that less than 50% of "optimized" pages resulted in more clicks. Even worse: 34 % of the changes led to a decrease in clicks!
It is therefore hugely important that optimizations made are measured to avoid "getting worse".
Here are some basic steps for possible SEO testing:
Determine what you want to measure and why you want to measure it.
Make a hypothesis. What do you expect to happen? What do you want to happen as a result of your changes?
Document your tests. Make sure that the tests can be reproduced reliably - only then can you be sure that you are measuring the right thing.
Publish your changes and submit the URLs to Google Search Console for review.
Run the test for a long enough period of time to confirm whether your hypothesis can be rejected or confirmed. Document your results and any other observations, such as competitor changes, that might affect the results.
Take appropriate action based on the results of your testing.
This process can be easily done and documented using a great Excel spreadsheet. Everything from the hypothesis to the URL to the measured values can be recorded in the spreadsheet.
10. Tracking and analyzing KPIs
If you decide to do SEO - which you really should - the following SEO KPIs are crucial, according to seonative:
Search engine rankings (overall and per page)
Click-through rate (CTR)
Traffic / page views from organic search
conversion rate
Bounce rate / engagement rate
Number of pages per session
Average session duration
Pre-conversion
Crawling and loading times
Visibility
Number of backlinks / domain popularity
Referral Traffic
The thing to remember about these KPIs is that they depend on your goals and objectives. Some may apply to your situation, others may not.
Consider this a good starting point to determine how you can best measure the success of a campaign.
Conclusion
Since content on the Internet has no expiration date, it grows at an enormous pace from day to day. So it also becomes more and more difficult for your web pages to be found in the search engines and for you to answer search queries with your content. Thus, web optimization demands more and more time and quickly you get lost in the many different optimization possibilities.
We hope that we can guide you a bit with the ten strategies in your web optimization and that you can now focus on the important factors in web optimization.
What exactly should I do now?!
Call us and we'll have a look together at where and how we can optimize your website.
